Lesson Example Discussion Quiz: Class Homework |
Example |
Title: Probability distribution function of discrete random variable |
Grade: 9-a Lesson: S4-L1 |
Explanation: The best way to understand statistics is by looking at some examples. Take turns and read each example for easy understanding. |
Examples:
A random variable X has the following probabaility distribution
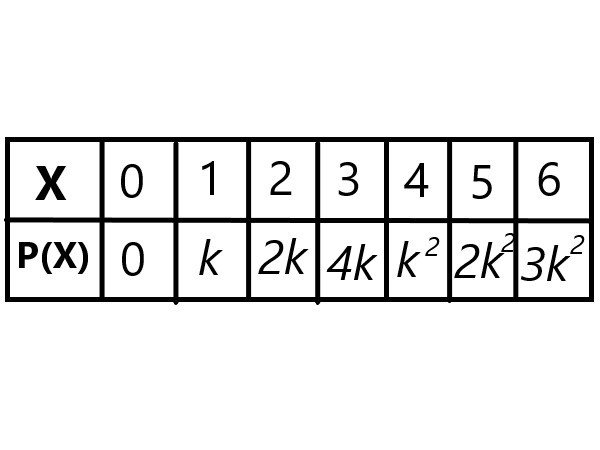 Determine k,P(x<3),P(0<x<3),P(x≥5)
Determine k,P(x<3),P(0<x<3),P(x≥5)
Step 1a
|
|
Finding the value of 'k' |
|
Explanation: Sum of probabilities = 1, X is a random variable. \$\sum_{i=0}^6 P(X) = 1\$ P(X=0)+P(X=1)+P(X=2)+P(X=3)+P(X=4)+P(X=5)+P(X=6) = 1 \$0 + k + 2k + 4k + k^2 + 2k^2 + 3k^2 = 1\$ \$7k + 6k^2 = 1\$ \$6k^2 + 7k - 1 = 0\$ \$6k^2 + 6k + k - 1 = 0\$ \$6k(k+1)-1(k+1) = 0\$ \$(6k-1)(k+1) = 0\$ \$k = 1/6 , k = -1\$ k is probability and it cannot be negative. \$k = 1/6 \$ |
|
Step 1b
|
|
Determine P(x<3) |
|
Explanation: P(x<3) = P(X=0) + P(X=1) + P(X=2) ⇒0 + k + 2k ⇒ 3k ⇒ \$3 × 1/6\$ \$P(x<3) = 1/2\$ \$P(x<3) = 0.5\$ |
|
Step 1c
|
|
Determine P(0<x<3) |
|
Explanation: P(0<x<3) = P(X=1) + P(X=2) ⇒ k + 2k ⇒ 3k ⇒ \$3 × 1/6\$ \$P(0<x<3) = 1/2\$ \$P(0<x<3) = 0.5\$ |
|
Step 1d
|
|
Determine P(x≥5) |
|
Explanation: P(x≥5) = P(X=5) + P(X=6) ⇒\$2k^2 + 3k^2\$ ⇒\$5k^2\$ ⇒\$5(1/6)^2\$ ⇒\$5 × 1/36\$ \$P(x≥5) = 5/36\$ \$P(x≥5) = 0.13\$ |
|
Copyright © 2020-2022 saibook.us Contact: info@saibook.us Version: 1.5 Built: 27-February-2023 06:00 AM EST