Lesson Example Discussion Quiz: Class Homework |
Example |
Title: Bowley’s Coefficient of skewness |
Grade: 9-a Lesson: S2-L8 |
Explanation: The best way to understand statistics is by looking at some examples. Take turns and read each example for easy understanding. |
Examples:
The weights of 8 people were recorded in kg as 35, 41, 42, 56, 58, 62, 90, 77. Find the percentile for the weight 58 kg.
Step 1a
|
|
Bulding the cumulative frequencies |
|
Explanation: |
|
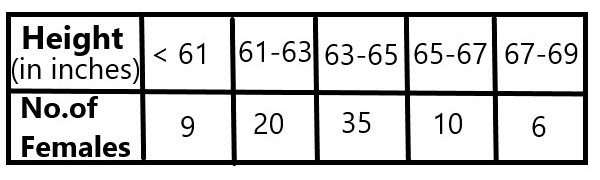
Height (in inches) ⇒ No.of females |
Cumulative frequency |
< 61 ⇒ 9 |
9 |
61-63 ⇒ 20 |
9+20 = 29 |
63-65 ⇒ 35 |
29+35 = 64 |
65-67 ⇒ 10 |
64+10 = 74 |
67-69 ⇒ 6 |
74+6 = 80 |
Step 1b
|
|
Calculating the quartiles \$Q_1,Q_2,Q_3\$ |
|
Explanation: \$Q_1 = N/4 = 80/4 = 20\$ \$Q_1\$ class is (61-63) \$l_1 = 61,l_2 = 63\$ ,c.f. = 9,f=20 \$Q_1 = l_1 + ((l_2-l_1)(N/4 - c.f.))/f\$ \$Q_1 = 61 + ((63-61)(20 - 9))/20\$ ⇒\$Q_1 = 62.1\$ \$Q_2 = "2N"/4 = 2*80/4 = 160/4 = 40\$ \$Q_2\$ class is (63-65) \$l_1 = 63,l_2 = 65\$ ,c.f. = 29,f=35 \$Q_2 = l_1 + ((l_2-l_1)(2N/4 - c.f.))/f\$ \$Q_2 = 63 + ((65-63)(40 - 29))/35\$ ⇒\$Q_2 = 63.62\$ \$Q_3 = "3N"/4 = 3*80/4 = 240/4 = 60\$ \$Q_3\$ class is (63-65) \$l_1 = 63,l_2 = 65\$ ,c.f. = 29,f=35 \$Q_3 = l_1 + ((l_2-l_1)(3N/4 - c.f.))/f\$ \$Q_3 = 63 + ((65-63)(60 - 29))/35\$ ⇒\$Q_3 = 64.77\$ |
|
Step 1c
|
|
Calculate skewness |
|
Explanation: skewness = \$(Q_3+Q_1-2Q_2)/(Q_3-Q_1)\$ substitute \$Q_1 = 62.1,Q_2 = 63.62,Q_3 = 64.77\$ in skewness \$SK_B = (64.77+62.1-2(63.62))/(64.77-62.1)\$ \$SK_B = -0.144\$ skewness < 0, i.e,\$Q_3-Q_2 < Q_2-Q_1\$ then the distribution or the curve is negatively skewed. |
|
Copyright © 2020-2022 saibook.us Contact: info@saibook.us Version: 1.5 Built: 13-March-2023 06:00 AM EST