Lesson Example Discussion Quiz: Class Homework |
Lesson |
Title: Angles |
Grade: 6-a Lesson: S2-L4 |
Explanation: Hello students, let us learn a new topic in geometry today with definitions, concepts, examples, and worksheets included. |
Lesson:
Definition: Interior Angle |
|
|
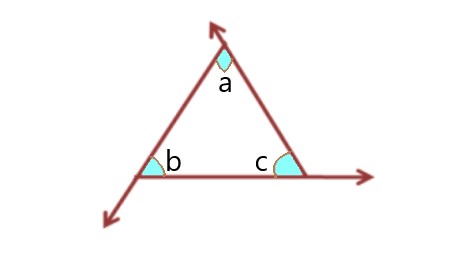
. |
Explanation: In this image, the angles ∠a, ∠b, and ∠c are interior angles. |
|
Definition: Exterior Angle |
|
|
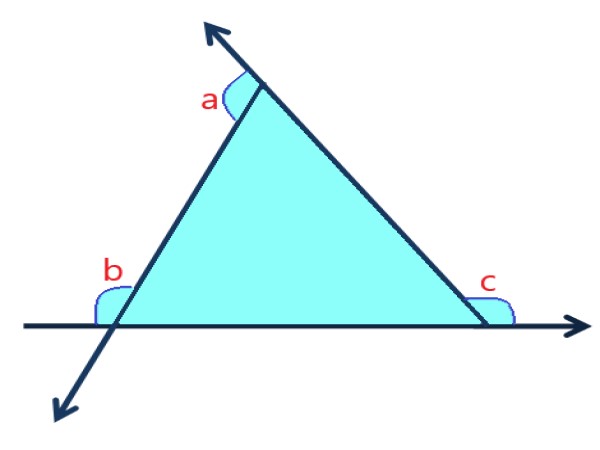
. |
Explanation: In this image, the angles ∠a, ∠b, and ∠c are exterior angles. |
|
Definition: Supplementary Angle |
|
|
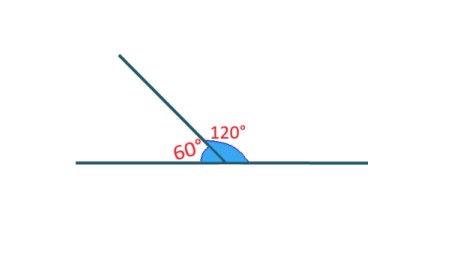
. |
Explanation: In the image, the angles with measures of 60 degrees and 120 degrees are supplementary angles because their sum is equal to 180 degrees. |
|
Definition: Complementary |
|
|
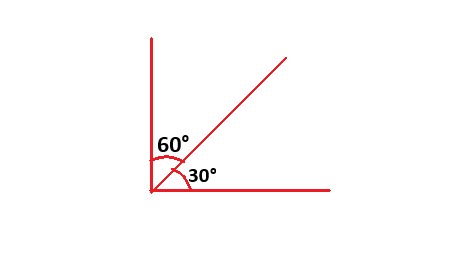
. |
Explanation: In the image, the angles with measures of 60 degrees and 30 degrees are complementary angles because their sum is equal to 90 degrees. |
|
Copyright © 2020-2024 saibook.us Contact: info@saibook.us Version: 1.5 Built: 12-March-2024 08:10 PM EST