Lesson Example Discussion Quiz: Class Homework |
Lesson |
Title: Trigonometry |
Grade: Best-SAT3 Lesson: S7-P2 |
Explanation: Hello students, let us learn a new topic in SAT-3 today with definitions, concepts, examples, and worksheets included. |
Lesson:
Definition: Trigonometry Equations |
|
. Trigonometry equations are mathematical expressions involving trigonometric functions such as sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent. . Trigonometric equations can involve solving for unknown angles or side lengths, manipulating trigonometric identities, and applying trigonometric functions to real-world situations. |
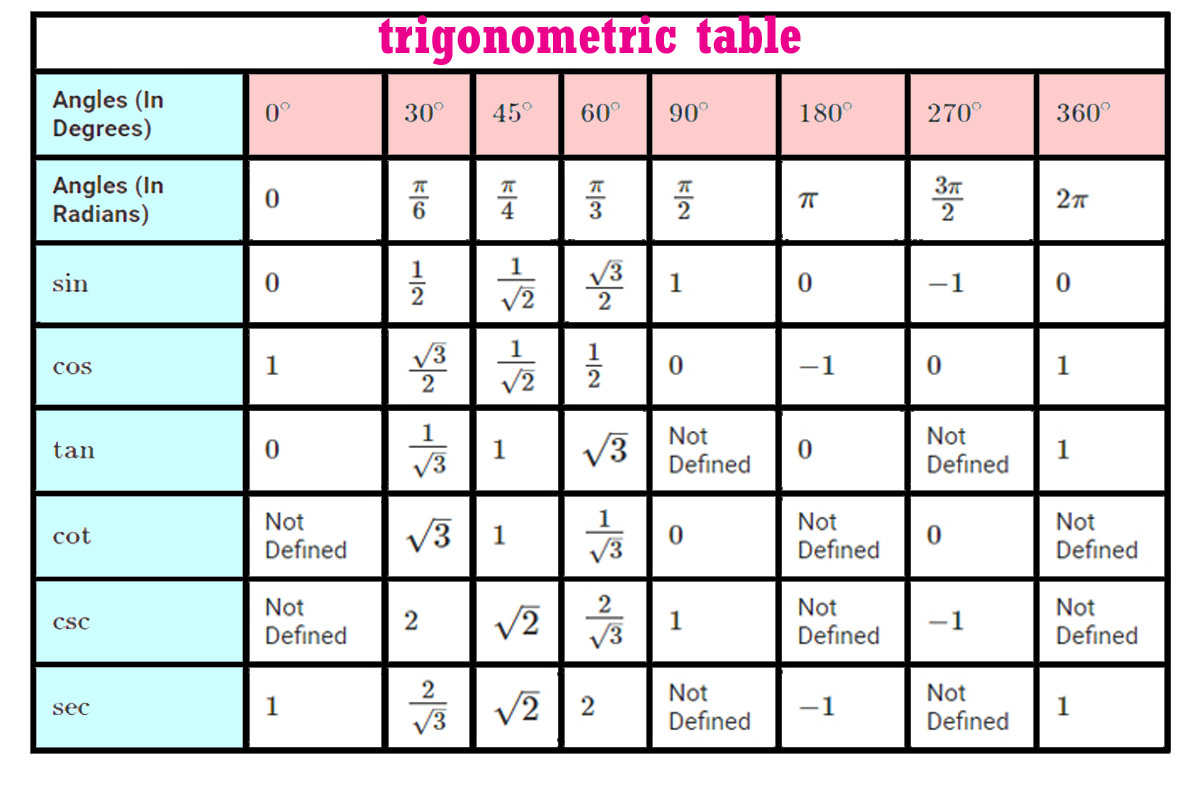
. |
Explanation: The image is likely a trigonometric table. It lists the values of sine, cosine, tangent, and other trig functions for various angles in degrees and radians. |
|
Definition: Conversion Between Radians and Degrees |
|
Conversion between radians and degrees refers to the mathematical process of translating an angle measurement from one unit to the other. Both radians and degrees are units used to measure angles, with degrees typically being used in everyday applications and radians in mathematical contexts like calculus and trigonometry. |
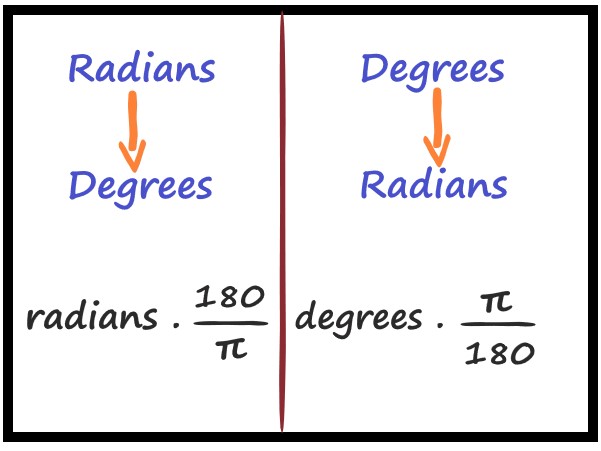
. |
Explanation:
1. Degrees to Radians: To convert degrees to radians, you can use the formula: \$ ""radians"" = (""degrees"" × π)/180 \$ This formula multiplies the degree value by π (approximately 3.14159) and then divides by 180.
\$ ""degrees"" = (""radians"" × 180)/π \$ This formula multiplies the radian value by 180 and then divides by π. |
|
Definition: Law Of Sines |
|
The Law of Sines is a mathematical formula used in trigonometry to relate the angles and sides of a triangle. It states that in any triangle, the ratio of the length of a side to the sine of its opposite angle is the same for all three sides. |
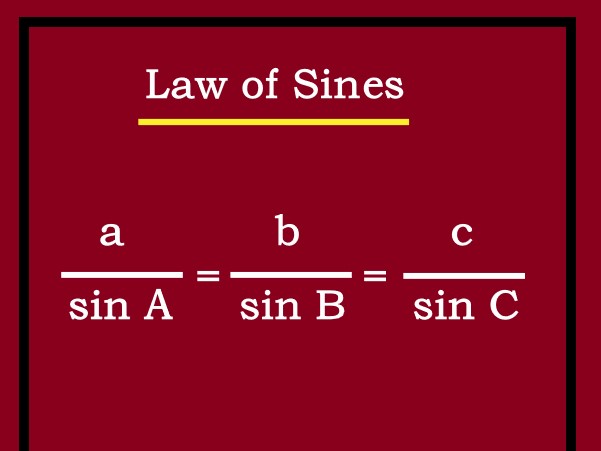
. |
Explanation: Where a,b, and c are the lengths of the sides of the triangle, and A, B, and C are the angles opposite these sides, respectively. The Law of Sines is particularly useful for solving triangles that are not right-angled. |
|
Definition: Law Of Cosines |
|
The Law of Cosines states that in any triangle, the square of one side is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, minus twice the product of those two sides and the cosine of the angle between them. Essentially, it is a generalization of the Pythagorean Theorem, which applies when you don’t have a right triangle. It allows you to find a missing side or angle when you have certain other information about the triangle. |
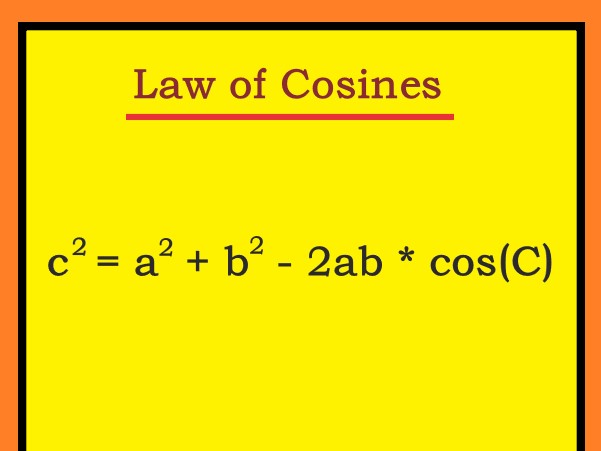
. |
Explanation: Where a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides of the triangle and C is the angle opposite the side c. |
|
Definition: Inverse Trigonometric Functions |
|
Inverse trigonometric functions are the functions that reverse the effect of the original trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent, etc.). They take a value from the trigonometric function and return the corresponding angle that produced that value. |
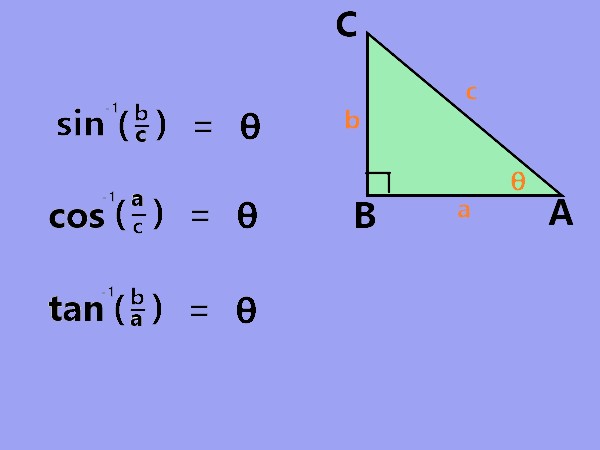
. |
Explanation: The image demonstrates inverse trigonometric functions help determine angles when triangle sides are known. |
|
Copyright © 2020-2022 saibook.us Contact: info@saibook.us Version: 1.5 Built: 09-October-2024 09:20AM EST