Lesson Example Discussion Quiz: Class Homework |
Lesson |
Title: Trignometry |
Grade: Best-SAT3 Lesson: S7-P1 |
Explanation: Hello students, let us learn a new topic in SAT-3 today with definitions, concepts, examples, and worksheets included. |
Lesson:
Definition: Trignometry Functions |
|
Trigonometric functions relate angles in a triangle to side lengths. Main functions are sine, cosine, and tangent (sin, cos, tan), used to calculate ratios in right triangles: sine relates opposite to hypotenuse, cosine relates adjacent to hypotenuse, and tangent relates opposite to adjacent side. |
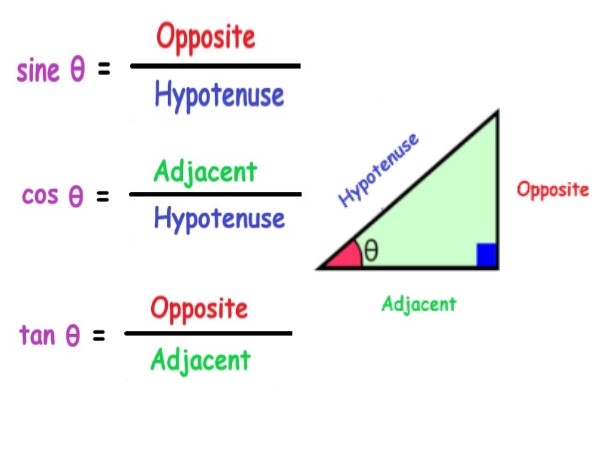
. |
Explanation: The image displays the trigonometric functions: sinθ, cosθ, and tanθ, along with their respective formulas. |
|
Definition: Trigonometric Ratios |
|
In a right-angled triangle, trigonometric ratios relate angles and sides. The primary ratios are sine (sin), cosine (cos), and tangent (tan). |
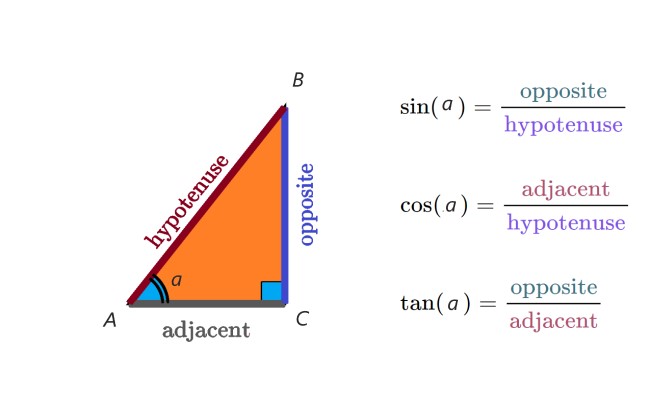
. |
Explanation: Trigonometric ratios are mathematical relationships that exist between the angles and sides of a right-angled triangle. These ratios express the connections between the lengths of specific sides and the measures of particular angles in the triangle. Simply put, trigonometric ratios are a set of rules that relate the angles and sides of a right-angled triangle to each other. |
|
Definition: Trigonometry Identities |
|
Trigonometric identities are equations that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the variables within their domains. |
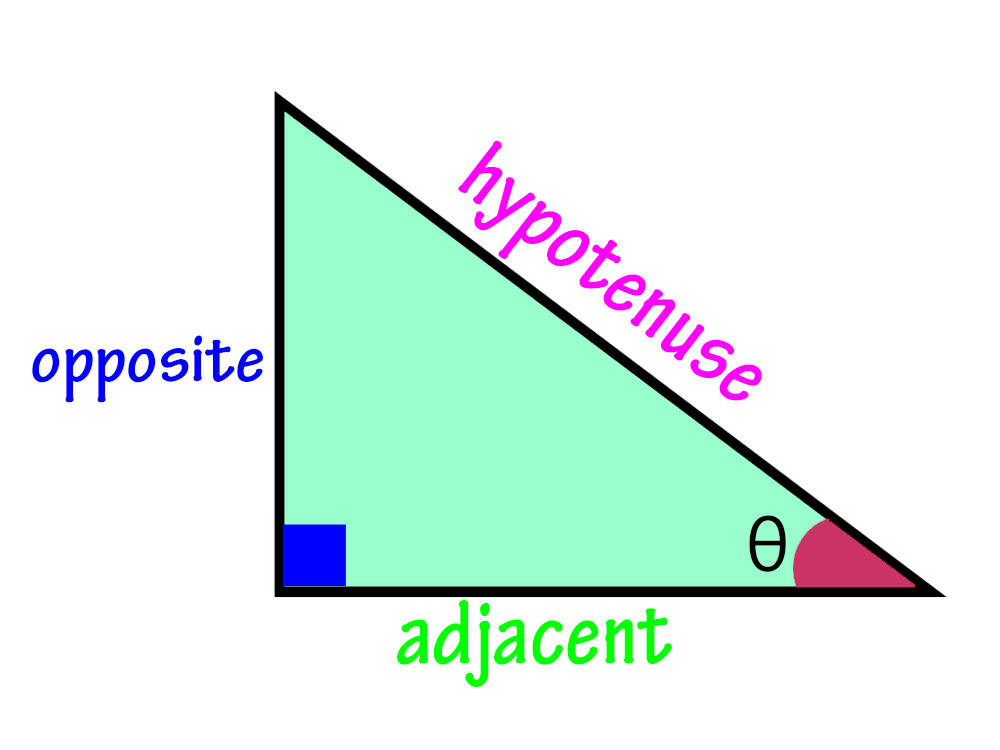
. |
Explanation: In trigonometry, a right triangle contains a 90-degree angle. Its sides are designated based on their connection to this angle: the hypotenuse, opposite, and adjacent sides, each playing a distinct role. |
|
Copyright © 2020-2022 saibook.us Contact: info@saibook.us Version: 1.5 Built: 09-October-2024 09:20AM EST