Lesson Example Discussion Quiz: Class Homework |
Lesson |
Title: Algebra |
Grade: Best-SAT3 Lesson: S5-P1 |
Explanation: Hello students, let us learn a new topic in SAT-3 today with definitions, concepts, examples, and worksheets included. |
Lesson:
Definition: Linear Equation |
|
A linear equation is an algebraic equation that represents a straight line on a coordinate plane.
It is an equation in which the highest power of the variable(s) is one.
The general form of a linear equation is: |
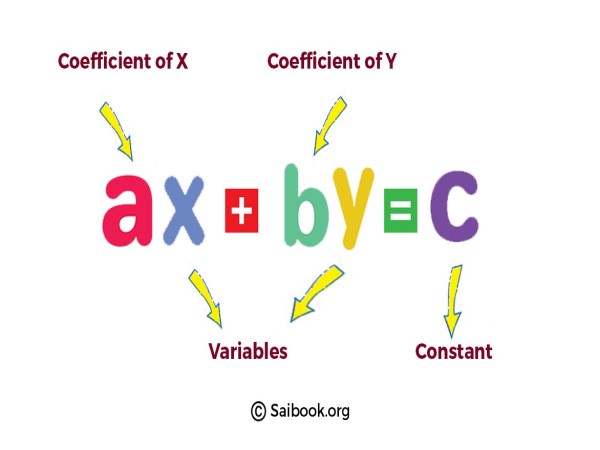
. |
Explanation: Here, the given image shows that x and y are variables. The constants a and b represent the coefficients of the variables x and y, respectively, while c is the constant term. |
|
Definition: Linear Functions |
|
A linear function is a mathematical function that can be represented by a straight line when graphed on a Cartesian coordinate system. It is an algebraic expression of the form |
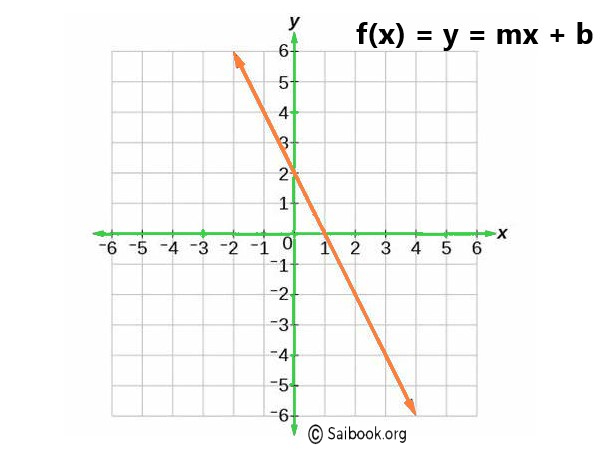
. |
Explanation:
The given image shows the linear function, so here |
|
Definition: Linear Inequalities |
|
Linear inequalities are mathematical statements that express a relationship between two algebraic expressions using inequality symbols (<, >, ≤, or ≥). These inequalities involve linear equations, which consist of variables raised to the first power, multiplied or divided by constants. The general form of a linear inequality is ax + b < c. |
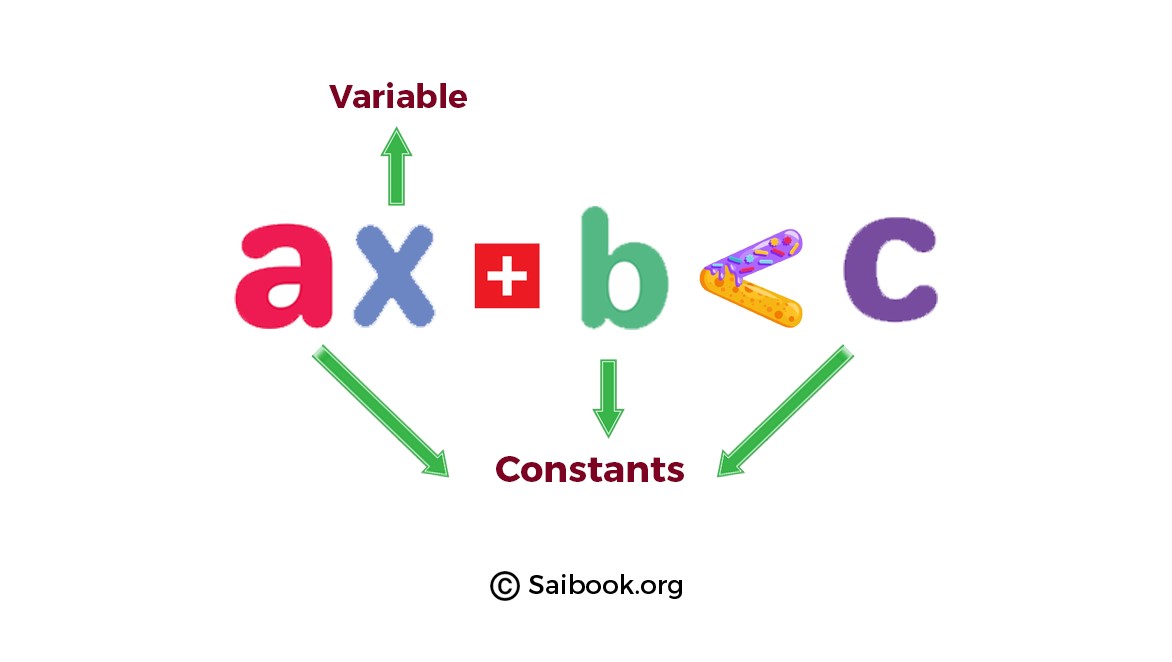
. |
Explanation: Here the given image shows the ax + b < c, where x represents the variable, a and b are constants, and c is a constant. |
|
Copyright © 2020-2022 saibook.us Contact: info@saibook.us Version: 1.5 Built: 09-October-2024 09:20AM EST