Lesson Example Discussion Quiz: Class Homework |
Lesson |
Title: Trigonometry Identities (quotient , co-function) |
Grade: 10-a Lesson: S3-L4 |
Explanation: Hello students, let us learn a new topic in SAT-2 today with definitions, concepts, examples, and worksheets included. |
Lesson:
Definition: Trigonometry Identities |
|
Trigonometric identities are equations that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the variables within their domains. |
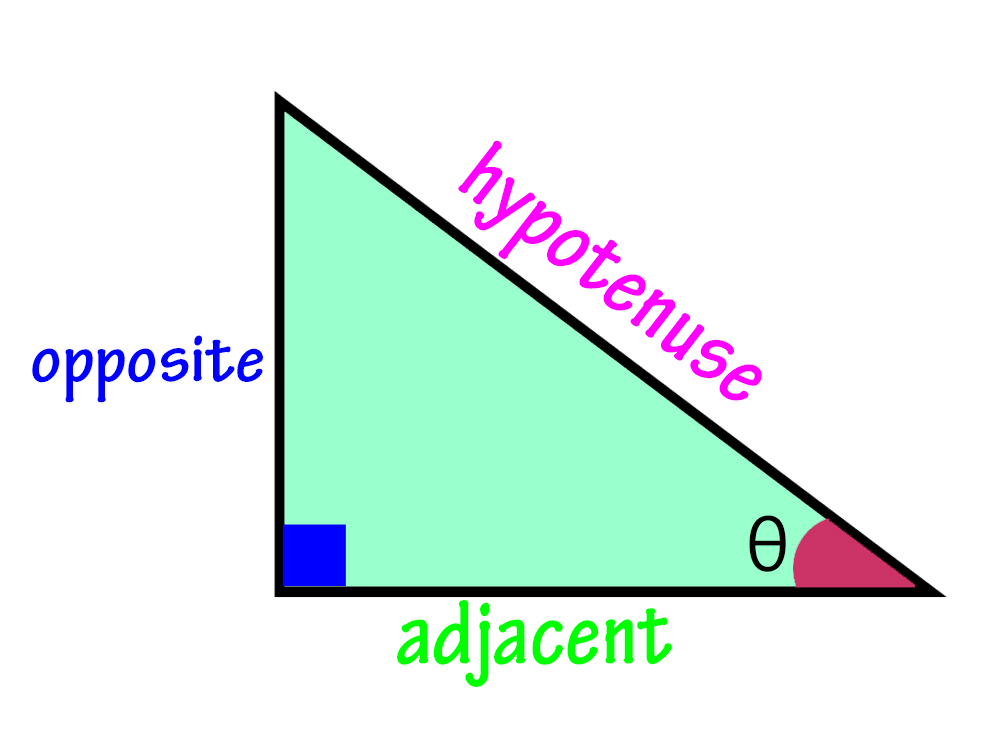
. |
Explanation: These identities are fundamental in trigonometry and are used to simplify expressions, solve equations, and prove other mathematical statements involving trigonometric functions. |
|
Definition: Quotient identities |
|
Quotient identities involve ratios of trigonometric functions. The most commonly used quotient identities involve the sine, cosine, and tangent functions. |
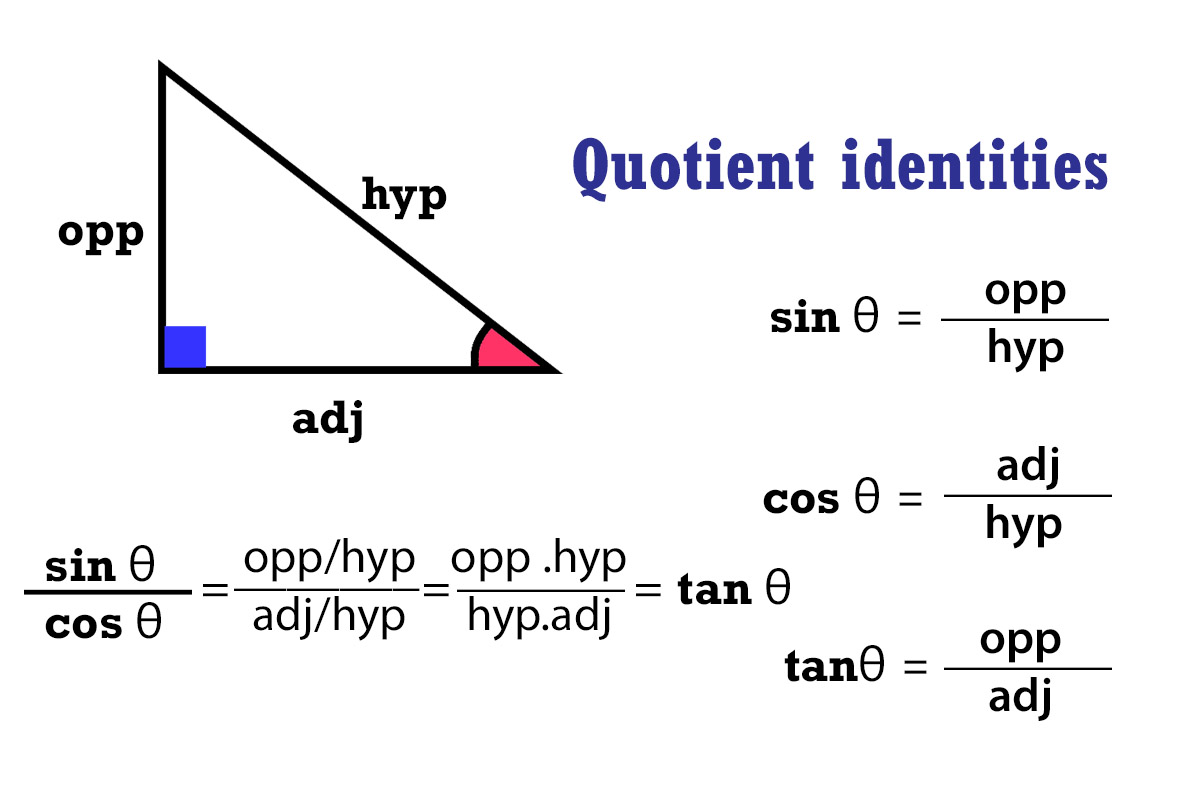
. |
Explanation:
The quotient of sine and cosine is tangent.
|
|
Definition: Co-function identities |
|
Co-function identities relate the trigonometric functions of complementary angles \$("angles whose sum is 90 degrees or" π/2 "radians")\$. |
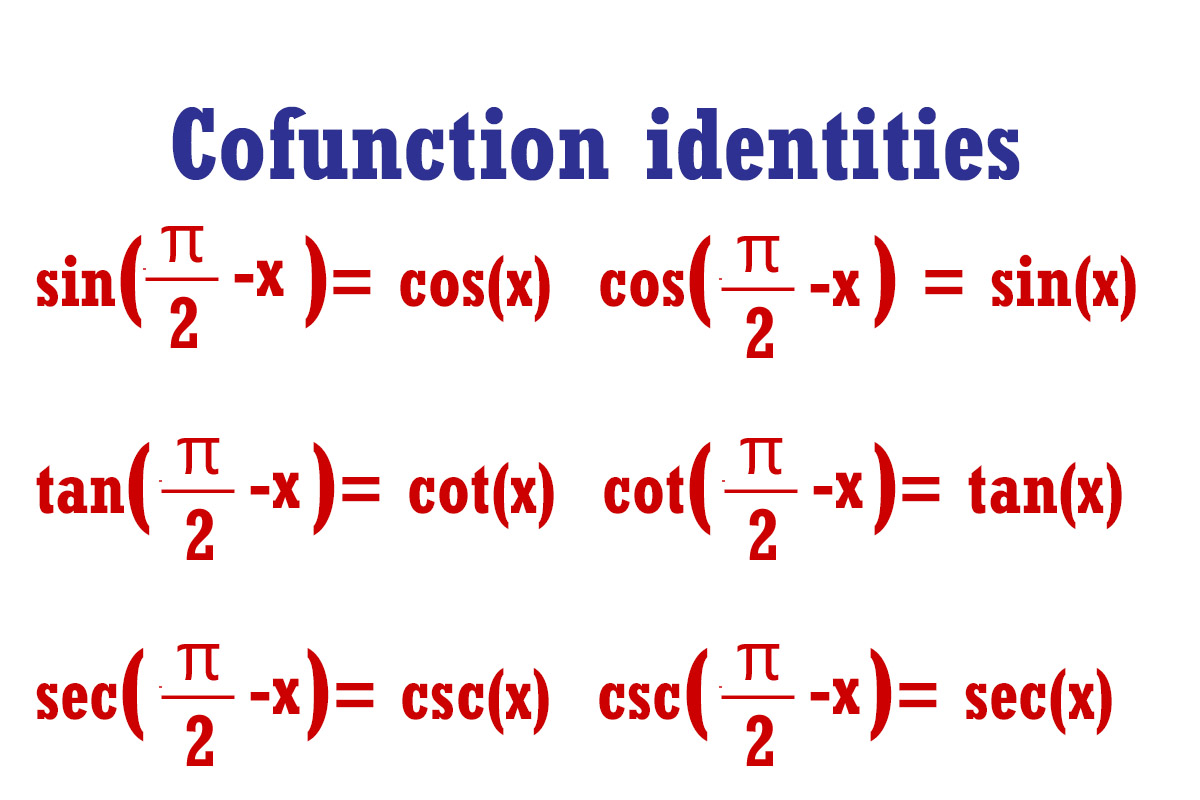
. |
Explanation:
Sine and Cosine Co-function Identity:
|
|
Copyright © 2020-2022 saibook.us Contact: info@saibook.us Version: 1.5 Built: 07-June-2024 09:20AM EST