Lesson Example Discussion Quiz: Class Homework |
Example |
Title: Multiplication Fractions |
Grade: 8-a Lesson: S1-L7 |
Explanation: Hello Students, time to learn examples. Let us take turns and read each example. Explain each step. Pay special attention to steps and pictures and communicate in your own words. |
Examples:
Multiplication \$5 28/14 \times 3 24/16\$.
Step 1a
|
|
First, convert the given mixed fractions into improper fractions. ⇒ Now multiply the denominator with a whole number and add the answer to the numerator. ⇒\$5 28/14\$ = \$98/14\$. ⇒\$3 24/16\$ = \$72/16\$. |
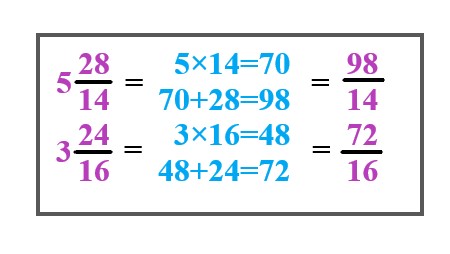
|
Explanation: Now multiply 5 by 14 and add 28 then We get 98. Now multiply 3 by 16 and add 24 then We get 72. We get the fractions \$ 98/14, 72/16 \$. |
|
Step 1b
|
|
Multiply \$98 \times 72\$ we get 7056. Multiply \$14 \times 16\$ we get 224 |
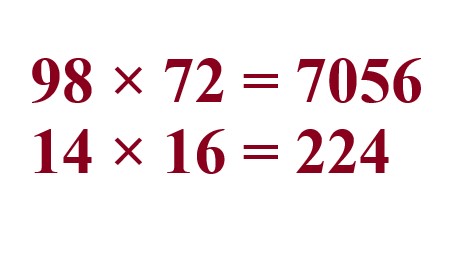
|
Explanation: Multiply the numerator with the numerator and the denominator with denominator. |
|
Step 1c
|
|
Reduce by dividing both the numerator and denominator \$\cancel(7056)^(63)/\cancel(224)^(2)\$ we get \$63/2\$. |
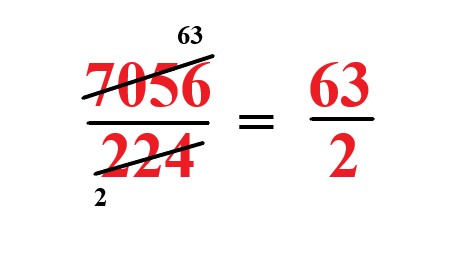
|
Explanation: Reduce by dividing both the numerator and denominator by using 112. |
|
Step 1d
|
|
Divide the fraction \$63/2\$. |
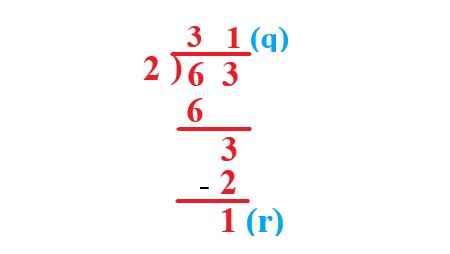
|
Explanation: By dividing 63 by 2 we get 31 as the quotient and the remainder as 1. |
|
Step 1e
|
|
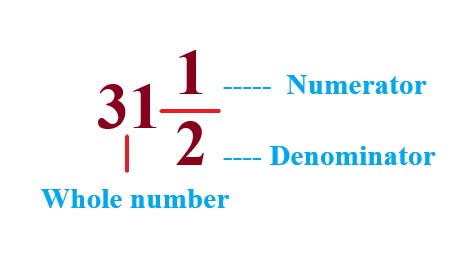
\$"Mixed fraction"\$ = \$"Whole number" + "Numerator" /"Denominator"\$ |
|
Explanation: Therefore, the mixed fraction \$31 1/2\$. |
|
Copyright © 2020-2022 saibook.us Contact: info@saibook.us Version: 1.5 Built: 28-June-2023 09:20AM EST