Lesson Example Discussion Quiz: Class Homework |
Example |
Title: Angles |
Grade: 6-a Lesson: S2-L3 |
Explanation: The best way to understand geometry is by looking at some examples. Take turns and read each example for easy understanding. |
Examples:
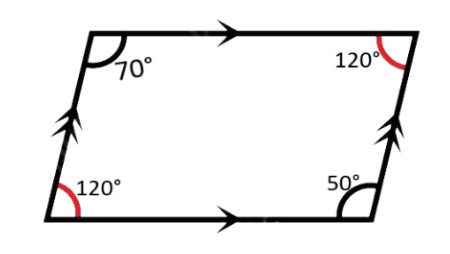
In a quadrilateral ABCD, the measures of ∠A, ∠B, and ∠C are 70º, 120º, and 50º, respectively. Find the measure of ∠D.
Step 1a
|
|
The sum of the angles in a quadrilateral is always 360º. To find the measure of ∠D, we subtract the sum of angles ∠A, ∠B, and ∠C from 360º. |
. |
Explanation: The sum of a quadrilateral’s angles equals 360º; ∠D = 360 - (∠A + ∠B + ∠C). |
|
Step 1b
|
|
∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 360º. Now plug the values 70º + 120º∘ + 50º∘ + ∠D = 360º. 240º + ∠D = 360º. |
|
Explanation: ∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 360º. Now plug in the values: 70º + 120º∘ + 50º∘ + ∠D = 360º. 240º + ∠D = 360º. |
|
Step 1c
|
|
∠D = 360º - 240º = 120º. Therefore, the measure of ∠D is 120º. |
|
Explanation: To find the measure of angle D, you need to subtract its known angle of 240 degrees from 360 degrees (a full circle). This gives us 120 degrees. |
|
Copyright © 2020-2024 saibook.us Contact: info@saibook.us Version: 1.5 Built: 21-March-2024 08:10 PM EST